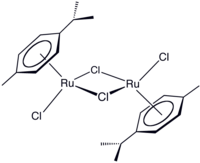
(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dichloro(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) dimer
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
52462-29-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
8297222 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.850 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H28Cl4Ru2 | |
| Molar mass | 612.38 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red solid |
| Melting point | 247 to 250 °C (477 to 482 °F; 520 to 523 K) (decomposes) |
| Slightly, with hydrolysis | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organometallic compound with the formula [(cymene)RuCl2]2. This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
The dimer is prepared by the reaction of the phellandrene with hydrated ruthenium trichloride. In solution, [(cymene)RuCl2]2 exchanges with other arenes, releasing free p-cymene.
(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer reacts with Lewis bases to give monometallic adducts:
Such monomers adopt pseudo-octahedral piano-stool structures.
Treatment of [(cymene)RuCl2]2 with the chelating ligand TsDPENH. The product (cymene)Ru(TsDPEN-H) is a catalyst for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation.
[(cymene)RuCl2]2 is also used to prepare catalysts (by monomerization with dppf) used in borrowing hydrogen catalysis, a catalytic reaction that is based on the activation of alcohols towards nucleophilic attack.
...
Wikipedia
