1,2-Dioxin
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
1,2-Dioxine
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.07 g·mol−1 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Dibenzodioxin |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
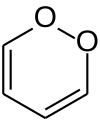
1,2-Dioxin is a heterocyclic, organic, antiaromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. It is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin (or p-dioxin).
Due to its peroxide-like characteristics, 1,2-dioxin is very unstable and has not been isolated. Even substituted derivatives are very labile, e.g. 1,4-diphenyl-2,3-benzodioxin. Indeed, in 1990, 3,6-bis(p-tolyl)-1,2-dioxin was wrongly accounted as the first stable derivative. It was subsequently shown that the initial compound was not a derivative of 1,2-dioxin, but a thermodynamically more stable dione.
The isomers 1,2-dioxin (left) and 1,4-dioxin (right)
Structure of the transient 1,4-diphenyl- 2,3-benzodioxin
Dioxin (1) and dione form (2)
...
Wikipedia