1893 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1893 Atlantic hurricane season |
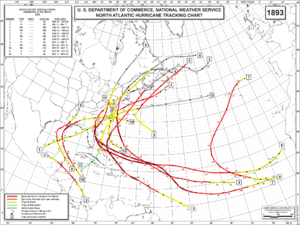
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
June 12, 1893 |
| Last system dissipated |
November 9, 1893 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
"Cheniere Caminada" |
| • Maximum winds |
135 mph (215 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure |
948 mbar (hPa; 27.99 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
12 |
| Total storms |
12 |
| Hurricanes |
10 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
5 |
| Total fatalities |
~4,028 |
| Total damage |
At least $6 million (1893 USD) |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1891, 1892, 1893, 1894, 1895
|
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 12 – June 19 |
| Peak intensity |
75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min) 1002 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 4 – July 7 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 13 – August 22 |
| Peak intensity |
120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) 986 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 24 |
| Peak intensity |
115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 952 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 19 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 30 |
| Peak intensity |
120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) 954 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 20 – August 29 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 4 – September 9 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 25 – October 14 |
| Peak intensity |
120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
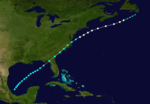
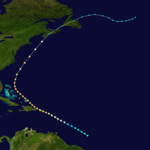
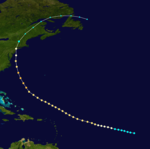
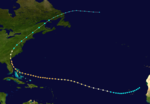
The 1893 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1893. The 1893 season was fairly active, with 12 tropical storms forming, 10 of which became hurricanes. Of those, 5 became major hurricanes. This season proved to be a very deadly season, with two different hurricanes each causing over two thousand (2000) deaths in the United States; at the time, the season was the deadliest in U.S. history. The season was one of two on the record, along with the 1998 Atlantic hurricane season, when 4 Atlantic hurricanes were active on the same day.
The season began early with its 1st storm forming on June 12 in the Bay of Campeche. The storm moved northeastward throughout its life, and hit the Florida Panhandle on June 16 as a strong tropical storm. After weakening over the Southeastern United States, the storm emerged over the Atlantic Ocean near Norfolk, Virginia. After briefly strengthening to a hurricane, the storm succumbed to cold water and shear and became extratropical on June 20.
July continued the season's activity, with a tropical storm forming in the western Caribbean Sea north of Panama on July 4. The 2nd storm of the season intensified to a 95 mph (153 km/h) hurricane before hitting the northeast coast of Honduras. It mainly retained its strength until it hit the northeastern coast of Belize on July 6. Afterwards, it rapidly weakened over the Yucatán Peninsula and dissipated on July 7. The storm sank several ships and reportedly caused a large loss of life. It has been paleotempestologically traced in sediment near Gales Point.
The 3rd storm of the season, known as the San Roque Hurricane, formed on August 13 east of the Lesser Antilles. It steadily strengthened to a hurricane while moving over the Leeward Islands. While approaching Puerto Rico on August 16, its winds increased to major hurricane status before landfall at Patillas. It crossed the island and exited near Isabela. There were heavy rains over the island of Puerto Rico and damages to the agricultural crops, especially coffee. In San Juan 2.36 inches of rain were reported. The eye remained over Puerto Rico for a period of seven hours. The lowest barometric pressure reading recorded in San Juan was 29.17 inches. Four deaths were reported. This was the first hurricane in Puerto Rico where flags were used to alert the public about the danger of an approaching hurricane; they were flown from government buildings.
...
Wikipedia