1964 Pacific typhoon season
| 1964 Pacific typhoon season |

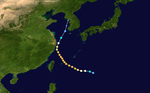
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
May 12, 1964 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 31, 1964 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Sally and Opal |
| • Maximum winds |
315 km/h (195 mph)
(1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure |
895 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
58 |
| Total storms |
39 official, 1 unofficial (record high)
|
| Typhoons |
26 (record high)
|
| Super typhoons |
7 |
| Total fatalities |
≥8,743 |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
| Related articles |
|
|
Pacific typhoon seasons
1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966
|
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 12 – May 23 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 960 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 16 – May 17 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) 1002 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 25 – May 26 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 21 – May 29 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 24 – July 4 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 968 hPa (mbar) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 27 – June 29 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (1-min) 1000 hPa (mbar) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 2 – July 7 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 960 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 5 – July 7 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 5 – July 11 |
| Peak intensity |
260 km/h (160 mph) (1-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
The 1964 Pacific typhoon season was the most active tropical cyclone season recorded globally, with a total of 40 tropical storms forming. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1964, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1964 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
The 1964 Pacific typhoon season was the most active season in recorded history with 39 storms. Notable storms include Typhoon Louise, which killed 400 people in the Philippines, Typhoons Sally and Opal, which had some of the highest winds of any cyclone ever recorded at 195 mph, Typhoons Flossie and Betty, which both struck the city of Shanghai, China, and Typhoon Ruby, which hit Hong Kong as a powerful 140 mph Category 4 storm, killing over 700 and becoming Hong Kong's worst named typhoon in history.
52 numbered tropical waves formed this year in the Western Pacific, of which 39 became tropical storms. 26 storms reached typhoon intensity, of which 7 reached super typhoon strength. The season's 39 tropical storms is the most recorded tropical storms to form in the basin. The South China Sea saw higher than normal activity in 1964 – between the years 1959-1963, the average was 3.2 typhoons to travel the area, compared to the 10 typhoons in the 1964 season. Two of the super typhoons, Sally and Opal, set seasonal records - Sally was strongest storm of the season, reaching a pressure of 894 mbar while Opal was the largest system of the season.
...
Wikipedia