Abdominal cavity
| Abdominal cavity | |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cavitas abdominis |
| MeSH | A01.047.025 |
| TA |
A01.1.00.051 A10.1.00.001 |
| FMA | 12266 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
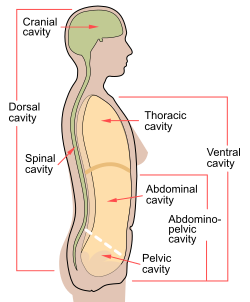
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet , opening into the pelvis.
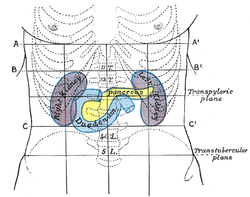
Organs of the abdominal cavity include the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, kidneys, large intestine, and adrenal glands.
The abdominal cavity is lined with a protective membrane termed the peritoneum. The inside wall is covered by the parietal peritoneum. The kidneys are located in the abdominal cavity behind the peritoneum, in the retroperitoneum. The viscera are also covered by visceral peritoneum.
Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity, which is a potential space. It contains serous fluid that allows motion. This motion is apparent of the gastrointestinal tract. The peritoneum, by virtue of its connection to the two (parietal and visceral) portions, gives support to the abdominal organs.
...
Wikipedia
