Alestramustine
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
|
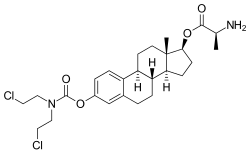
| Synonyms | Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(L-alaninate); Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(2β-aminopropanoate); Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-((2S)-2-aminopropanoate) |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H36Cl2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 511.48104 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Alestramustine (INN), also known as estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(L-alaninate), is a nitrogen mustard alkylating antineoplastic drug that was never marketed. It is the L-alanine ester of estramustine, which is a combination of the nitrogen mustard normustine coupled via a carbamate to the estrogen estradiol. Alestramustine acts as a prodrug to estramustine, and also forms estradiol as a byproduct. The drug, via its active metabolites, binds to microtubule-associated proteins and β-tubulin and interferes with microtubule function, thereby inhibiting cell division. Due to its estrogen moiety, alestramustine is selectively concentrated in estrogen receptor-positive cells such as prostate and breast.
...
Wikipedia
