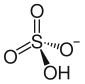
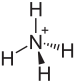Ammonium bisulfate
|
|
|||
 |
|||
 |
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Ammonium hydrogen sulfate
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
7803-63-6 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider |
23057 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.332 | ||
| PubChem | 16211166 | ||
| RTECS number | WS990000 | ||
| UNII |
8MW949D9GE |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| (NH4)HSO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 115.11 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.78 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 147 °C (297 °F; 420 K) | ||
| Very soluble | |||
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in methanol insoluble in acetone |
||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Other anions
|
Ammonium thiosulfate Ammonium sulfite Ammonium sulfate Ammonium persulfate |
||
|
Other cations
|
Sodium bisulfate Potassium bisulfate |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Ammonium bisulfate, also known as ammonium hydrogen sulfate, is a white, crystalline solid with the formula (NH4)HSO4. It is the product of the half-neutralization of sulfuric acid by ammonia.
It is commonly collected as a byproduct of the "acetone cyanohydrin route" to the commodity chemical methyl methacrylate.
It can also be obtained by hydrolysis of sulfamic acid in aqueous solution, which produces the salt in high purity:
It also arises by the thermal decomposition of ammonium sulfate:
It can be further neutralized with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate, a valuable fertilizer. It can be used as a weaker alternative to sulfuric acid, although sodium bisulfate is much more common.
...
Wikipedia