Aspergillomarasmine A
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(R-(R*,R*))-N-(2-((2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)amino)-2-carboxyethyl)-L-aspartic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H17N3O8 | |
| Molar mass | 307.257 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
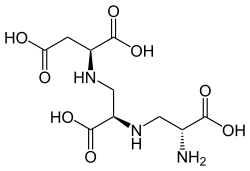
Aspergillomarasmine A is an polyamino acid naturally produced by the mold Aspergillus versicolor. The substance has been reported to inhibit two antibiotic resistance carbapenemase proteins in bacteria, New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 (NDM-1) and Verona integron-encoded metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM-2), and make those antibiotic-resistant bacteria susceptible to antibiotics. Aspergillomarasmine A is toxic to leaves of barley and other plants, being termed as "Toxin C" when produced by Pyrenophora teres.
The molecule is a tetracarboxylic acid with four -COOH groups. One section of the molecule is the amino acid aspartic acid. This has two alanine molecules attached. Aspergillomarasmine B differs in that the last alanine is replaced by glycine.
The crystalline substance was first isolated in 1956, but its name was given until 1965.
In addition to Aspergillus versicolor, aspergillomarasmine A is also produced by the ascomycete Pyrenophora teres where it acts as a toxin in the barley net-spot blotch disease. In P. teres, a biosynthetic precursor of aspergillomarasmine A, L,L-N-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-aspartic acid has also been isolated and found to contribute to the phytotoxic properties of this microbe. This precursor, aspergillomarasmine A itself, and a lactam form (anhydroaspergillomarasmine A) are together termed the marasmines.
Other producers of aspergillomarasmine A include Aspergillus flavus,Aspergillus oryzae,Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, and Fusarium oxysporum.
...
Wikipedia
