Atenolol
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tenormin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684031 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral or IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40–50% |
| Protein binding | 6–16% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic <10% |
| Biological half-life | 6–7 hours |
| Excretion |
Renal Lactic (In lactiferous females) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.941 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
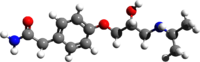
| Formula | C14H22N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 266.336 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
Atenolol is a selective β1 receptor antagonist, a drug belonging to the group of beta blockers (sometimes written β-blockers), a class of drugs used primarily in cardiovascular diseases. Introduced in 1976, atenolol was developed as a replacement for propranolol in the treatment of hypertension. It works by slowing down the heart and reducing its workload. Unlike propranolol, atenolol does not readily pass through the blood–brain barrier, thus decreasing the incidence of central nervous system side effects.
Atenolol is one of the most widely used β-blockers in the United Kingdom and was once the first-line treatment for hypertension. Atenolol is effective at reducing blood pressure, but recent studies indicate that it does not reduce the morbidity or mortality caused by hypertension, and may even increase mortality in some subgroups. This means that when people take this drug, they get better blood pressure numbers, but they still die of heart attacks and strokes, despite the lower blood pressure.
In addition, the role for β-blockers in general in hypertension was downgraded in June 2006 in the United Kingdom, and later in the United States, as they are less appropriate than newer blood pressure medications including calcium channel blockers, thiazide diuretics, angiotension converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotension receptor blockers, particularly in the elderly.
Atenolol is used for a number of conditions including hypertension, angina, long QT syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.
...
Wikipedia
