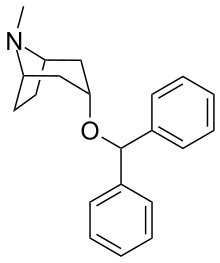
Benztropine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cogentin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 12-24 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | Benztropine |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H25NO |
| Molar mass | 307.429 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benzatropine (INN), also known as benztropine (USAN, BAN), is an anticholinergic marketed under the trade name Cogentin which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, Parkinsonism, and dystonia.
Benzatropine is an anticholinergic drug used in patients to reduce the side effects of antipsychotic treatment. Benzatropine is also a second-line drug for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It improves tremor, but not rigidity and bradykinesia. Benzatropine is also sometimes used for the treatment of dystonia, a rare disorder that causes abnormal muscle contraction, resulting in twisting postures of limbs, trunk, or face. In veterinary medicine, benzatropine is used to treat priapism in stallions.
These are principally anticholinergic:
While some studies suggest that use of anticholinergics increases the risk of tardive dyskinesia (a long-term side effect of antipsychotics), other studies have found no association between anticholinergic exposure and risk of developing tardive dyskinesia, although symptoms may be worsened.
Drugs that decrease cholinergic transmission may impair storage of new information into long-term memory. Anticholinergic agents can also impair time perception.
Benzatropine is a centrally acting anticholinergic/antihistamine agent. It is a selective M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Benzatropine partially blocks cholinergic activity in the basal ganglia and has also been shown to increase the availability of dopamine by blocking its reuptake and storage in central sites, and as a result, increasing dopaminergic activity. Animal studies have indicated that anticholinergic activity of benzatropine is approximately one-half that of atropine, while its antihistamine activity approaches that of mepyramine. Its anticholinergic effects have been established as therapeutically significant in the management of Parkinsonism. Benzatropine antagonizes the effect of acetylcholine, decreasing the imbalance between the neurotransmitters acetylcholine and dopamine, which may improve the symptoms of early Parkinson's disease.
...
Wikipedia
