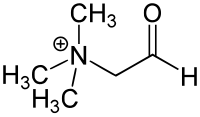
Betaine aldehyde
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
N,N,N-trimethyl-2-oxoethanaminium
|
|
| Other names
Betaine aldehyde
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H12NO | |
| Molar mass | 102.16 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Glycine betaine aldehyde, often simply called betaine aldehyde, is an intermediate in the metabolism of glycine, serine and threonine. The human aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) stimulates the transformation of betaine aldehyde to glycine betaine. Betaine aldehyde is a substrate for choline dehydrogenase (mitochondrial).
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a short chain aldehyde and quaternary ammonium compound. It can be considered a derivative of the amino acid glycine. Its chemical formula is C5H12NO+.
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a component of glycine, serine and threonine metabolism. It also serves as an osmolyte.
It can be found in cytoplasm and within the kidney, neurons, and stratum corneum.
...
Wikipedia
