Brahmaputra river
| Brahmaputra ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ |
|
| River | |
|
The Brahmaputra in Guwahati, Assam, India.
|
|
| Name origin: Sanskrit for Son (Putra) of Brahmā | |
| Countries |
|
|---|---|
| States | Assam, Arunachal Pradesh |
| Autonomous Region | Tibet |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Dibang River, Lohit River, Dhansiri River, Kolong River |
| - right | Kameng River, Manas River, Raidak River, Jaldhaka River, Teesta River, Subansiri River |
| City | Guwahati, Dibrugarh, Tezpur |
| Source | Angsi Glacier |
| - location | Himalayas, Tibet |
| - elevation | 5,210 m (17,093 ft) |
| - coordinates | 30°23′N 82°0′E / 30.383°N 82.000°E |
| Mouth | Bay of Bengal |
| - location | Ganga Delta, Bangladesh |
| - elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| - coordinates | 25°13′24″N 89°41′41″E / 25.22333°N 89.69472°ECoordinates: 25°13′24″N 89°41′41″E / 25.22333°N 89.69472°E |
| Length | 2,900 km (1,800 mi) |
| Basin | 651,334 km2 (251,500 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 19,300 m3/s (681,600 cu ft/s) |
| - max | 100,000 m3/s (3,531,500 cu ft/s) |
|
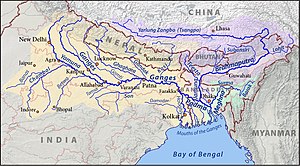
Map of the combined drainage basins of the Brahmaputra (violet), Ganga (orange), and Meghna (green).
|
|
The Brahmaputra (/ˌbrɑːməˈpuːtrə/ [brɔmmɔput̪rɔ nɔd̪] is one of the major rivers of Asia, a trans-boundary river which flows through China, India and Bangladesh. As such, it is known by various names in the region. In Bengali: ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ নদী, Brôhmôputrô; Sanskrit: ब्रह्मपुत्र, IAST: Brahmaputra; Tibetan: ་, Wylie: yar klung gtsang po Yarlung Tsangpo; simplified Chinese: 布拉马普特拉河; traditional Chinese: 布拉馬普特拉河; pinyin: Bùlāmǎpǔtèlā Hé. It is also called Tsangpo-Brahaputra (when referring to the whole river including the stretch within Tibet), and the Jamuna River in Bangladesh. The Manas River that runs through Bhutan joins it at Jogighopa, in India. It is the tenth largest river in the world by discharge, and the 29th longest.
...
Wikipedia