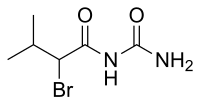
Bromisoval
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(RS)-2-Bromo-N-carbamoyl-3-methylbutanamide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.115 |
| EC Number | 207-825-7 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Bromisovalum |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H11BrN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 223.07 g·mol−1 |
| log P | 1.057 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.536 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.461 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N05CM03 (WHO) | |
| Oral | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related ureas
|
Carbromal |
|
Related compounds
|
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Bromisoval (INN), commonly known as bromovalerylurea, is a hypnotic and sedative of the bromoureide group discovered by Knoll in 1907 and patented in 1909. It is marketed over the counter in Asia under various trade names (such as Brovarin), usually in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Chronic use of bromisoval has been associated with bromine poisoning.
Bromovisal can be prepared by bromination of isovaleric acid by the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction followed by reaction with urea.
...
Wikipedia
