Chicago Aurora and Elgin Railroad
 |
|
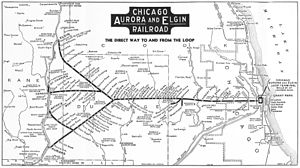
Map of the Chicago Aurora and Elgin Railroad from a 1936 public timetable folder
|
|
| Locale | Chicago, Illinois and western suburbs |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1902–1959 |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Headquarters | Wheaton, Illinois |
The Chicago Aurora and Elgin Railroad (CA&E), known colloquially as the "Roarin' Elgin" or the "Great Third Rail", was an interurban railroad that operated passenger and freight service on its line between Chicago, Illinois and Aurora, Batavia, Geneva, St. Charles, and Elgin. The railroad also operated a small branch to Mt. Carmel Cemetery in Hillside and owned a branch line to Westchester.
Wounded by the increased use of automobiles after World War II, the CA&E abruptly ended passenger service in 1957. Freight service was suspended in 1959, and the railroad was officially abandoned in 1961. Most of the right-of-way has since been converted to the Illinois Prairie Path rail trail.
The first known attempt to create an electric railway between the metropolis of Chicago and the Fox Valley settlement of Aurora was in late 1891. By this time, passengers in Aurora and Elgin were served by steam engines. Elgin was served by the Milwaukee Road. Geneva and West Chicago served by the Chicago and North Western Railway. St. Charles served by The Chicago and Great Western. And, Aurora was served by the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy (CB&Q). However, it was thought that an electric line would greatly facilitate interurban travel, as there would be no freight trains to slow passenger trains. A group of investors founded the Chicago & Aurora Interurban Railway with a $1 million investment. However, the railroad was unable to secure additional funds; it failed to meet an 1893 construction deadline and effectively ceased operation thereafter. A second attempt came two years later with the Chicago, Elgin & Aurora Electric Railway. Plans called for the railroad to run through Turner (now West Chicago), Wheaton, and Glen Ellyn. Like its predecessor, the railroad failed to acquire the necessary funds for construction. Yet another group incorporated the DuPage Interurban Electric Railway in 1897, but was met with a similar fate. Small electric lines opened in the 1890s that connected the municipalities of the Fox River Valley. A profitable streetcar railway stretched from Aurora north to Carpentersville. The success of this railway inspired investors to again attempt an electric connection to Chicago. A group led by F. Mahler, E. W. Moore, Henry A. Everett, Edward Dickinson, and Elmer Barrett formed independent railway lines that were projected to stretch from Aurora and Elgin to Chicago. These two companies were incorporated on February 24, 1899. The Everett-Moore group was Ohio's largest interurban railroad company and had experience administrating several lines around Cleveland, most notably the Lake Shore Electric Railway. These two companies, the Aurora, Wheaton & Chicago Railway and Elgin & Chicago Railway, were incorporated on February 24, 1899.
...
Wikipedia
