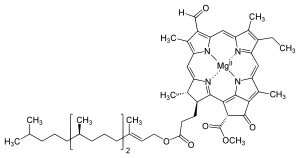
Chlorophyll d
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| E number | E140 (colours) |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C54H70MgO6N4 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Chlorophyll d is a form of chlorophyll, identified by Harold Strain and Winston Manning in 1943. It is present in marine red algae and cyanobacteria which use energy captured from sunlight for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll d absorbs far-red light, at 710 nm wavelength, just outside the optical range. An organism that contains chlorophyll d is adapted to an environment such as moderately deep water, where it can use far red light for photosynthesis, although there is not a lot of visible light.
...
Wikipedia
