Common bile duct stones
| Common bile duct stone | |
|---|---|
 |
|
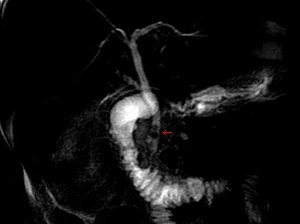
| MRCP image of two stones in the distal common bile duct | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | Xxx.x |
| ICD-9-CM | xxx |
Common bile duct stone, also known as choledocholithiasis, is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (thus + ). This condition causes jaundice and liver cell damage, and it requires treatment by cholecystectomy and/or ERCP.
Murphy's sign is commonly negative on physical examination in choledocholithiasis, helping to distinguish it from cholecystitis. Jaundice of the skin or eyes is an important physical finding in biliary obstruction. Jaundice and/or clay-colored stool may raise suspicion of choledocholithiasis or even gallstone pancreatitis. If the above symptoms coincide with fever and chills, the diagnosis of ascending cholangitis may also be considered.
Greater than 70% of people with gallstones are asymptomatic and are found incidentally on ultrasound. Studies have shown that 10% of those people will develop symptoms within five years of diagnosis and 20% within 20 years.
While stones can frequently pass through the common bile duct (CBD) into the duodenum, some stones may be too large to pass through the CBD and may cause an obstruction. One risk factor for this is duodenal diverticulum.
This obstruction may lead to jaundice, elevation in alkaline phosphatase, increase in conjugated bilirubin in the blood and increase in cholesterol in the blood. It can also cause acute pancreatitis and ascending cholangitis.
Choledocholithiasis (stones in common bile duct) is one of the complications of cholelithiasis (gallstones), so the initial step is to confirm the diagnosis of cholelithiasis. Patients with cholelithiasis typically present with pain in the right-upper quadrant of the abdomen with the associated symptoms of nausea and vomiting, especially after a fatty meal. The physician can confirm the diagnosis of cholelithiasis with an abdominal ultrasound that shows the ultrasonic shadows of the stones in the gallbladder.
The diagnosis of choledocholithiasis is suggested when the liver function blood test shows an elevation in bilirubin and serum transaminases. Other indicators include raised indicators of ampulla of vater (pancreatic duct obstruction) such as lipases and amylases. In prolonged cases the INR may change due to a decrease in vitamin K absorption. (It is the decreased bile flow which reduces fat breakdown and therefore absorption of fat soluble vitamins). The diagnosis is confirmed with either an MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography), an ERCP, or an intraoperative cholangiogram. If the patient must have the gallbladder removed for gallstones, the surgeon may choose to proceed with the surgery, and obtain a cholangiogram during the surgery. If the cholangiogram shows a stone in the bile duct, the surgeon may attempt to treat the problem by flushing the stone into the intestine or retrieve the stone back through the cystic duct.
...
Wikipedia
