Cyclophilin
| peptidylprolyl isomerase A (cyclophilin A) | |
|---|---|
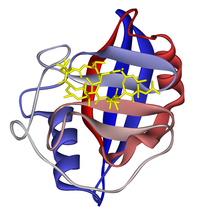
Ribbon diagram of cyclophilin A in complex with ciclosporin (yellow). From PDB: 1CWA.
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | PPIA |
| Entrez | 5478 |
| HUGO | 9253 |
| OMIM | 123840 |
| RefSeq | NM_203430 |
| UniProt | Q3KQW3 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 5.2.1.8 |
| Locus | Chr. 7 p13 |
| Pro_isomerase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

x-ray structure of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase a, ppia, rv0009, from mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Pro_isomerase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00160 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0475 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002130 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00154 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1cyh | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1cyh | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
Cyclophilins are a family of proteins from vertebrates and other organisms that bind to ciclosporin (cyclosporin A), an immunosuppressant which is usually used to suppress rejection after internal organ transplants. These proteins have peptidyl prolyl isomerase activity, which catalyzes the isomerization of peptide bonds from trans form to cis form at proline residues and facilitates protein folding.
Cyclophilin A is a cytosolic and highly abundant protein. The protein belongs to a family of isozymes, including cyclophilins B and C, and natural killer cell cyclophilin-related protein. Major isoforms have been found throughout the cell, including the ER, and some are even secreted.
Cyclophilin A also known as peptidylprolyl isomerase A, which is found in the cytosol, has a beta barrel structure with two alpha helices and a beta-sheet. Other cyclophilins have similar structures to cyclophilin A. The cyclosporin-cyclophilin A complex inhibits a calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphatase, calcineurin, the inhibition of which is thought to suppress organ rejection by halting the production of the pro-inflammatory molecules TNF alpha and interleukin 2.
...
Wikipedia
