Dentofacial osteotomy
| Orthognathic surgery | |
|---|---|
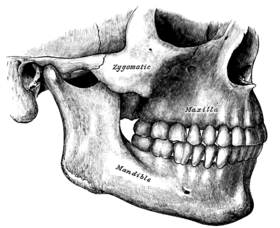
Relationship between mandible and maxilla
|
|
| ICD-9-CM | 76.6 |
Orthognathic surgery (/ˌɔːrθəɡˈnæθɪk/ OR-thəg-NATH-ik), also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and face related to structure, growth, sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems owing to skeletal disharmonies, or other orthodontic problems that cannot be easily treated with braces. Originally coined by Harold Hargis, this surgery is also used to treat congenital conditions such as cleft palate. Typically during oral surgery, bone is cut, moved, modified, and realigned to correct a dentofacial deformity. The word "osteotomy" means the division, or excision of bone. The dental osteotomy allows surgeons to visualize the jawbone, and work accordingly.
The operation is used to correct jaw problems in about 5% of general population presenting with dentofacial deformities like maxillary prognathisms, mandibular prognathisms, open bites, difficulty chewing, difficulty swallowing, temporomandibular joint disorder pains, excessive wear of the teeth, and receding chins. Many surgeons prefer this procedure for the correction of a dentofacial deformity due to its effectiveness.
It is estimated that nearly 5% of the UK or USA population present with dentofacial deformities that are not amenable to orthodontic treatment requiring orthognathic surgery as a part of their definitive treatment. Orthognathic surgery can be used to correct:
...
Wikipedia
