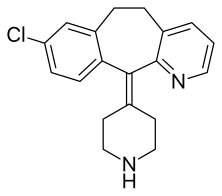
Desloratadine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Clarinex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Rapidly absorbed |
| Protein binding | 85% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 27 hours |
| Excretion | 40% as conjugated metabolites into urine Similar amount into the feces |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.166.554 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 310.82 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Desloratadine is a tricyclic H1-antihistamine that is used to treat allergies. It is an active metabolite of loratadine.
Desloratadine is used to treat allergic rhinitis and nasal congestion. It is the major metabolite of loratadine and the two drugs are similar in safety and effectiveness. Desloratadine is available in many dosage forms and under many trade names worldwide.
An emerging indication for desloratadine is in the treatment of acne, as an inexpensive adjuvant to isotretinoin and possibly as maintenance therapy or monotherapy.
Most common side-effects are fatigue, dry mouth, headache, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Desloratadine is a selective H1-antihistamine which functions as an inverse agonist at the histamine H1 receptor;
It is also an antagonist at all subtypes of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
It exhibits only peripheral activity since it does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier; hence, it does not cause drowsiness because it does not readily enter the central nervous system.
It has a long-lasting effect and is effective in moderate and low doses.
...
Wikipedia
