Diazald
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
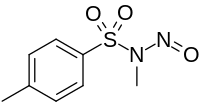
IUPAC name
N-Methyl-N-nitroso-p-toluenesulfonamide
|
|
| Other names
Diazald, N-methyl-N-nitroso-4-methylbenzenesulphonamide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.139 |
| EC Number | 201-252-6 |
| MeSH | C418734 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H10N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 214.24 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | light yellow solid |
| Melting point | 61–62 °C (142–144 °F; 334–335 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | skin sensitiser, irritant, explosive |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
N-Methyl-N-nitroso-p-toluenesulfonamide, known commercially as Diazald, is used as a relatively safe and easily handled precursor to diazomethane, which is toxic and unstable.
Upon the addition of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, an elimination reaction occurs to produce diazomethane as well as p-toluenesulfonic acid as a side product, according to the following mechanism:
...
Wikipedia


