Echinodon
|
Echinodon Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, 140 Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
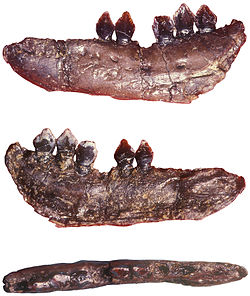
| Specimen NHMUK 48215b | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | †Ornithischia |
| Family: | †Heterodontosauridae |
| Genus: |
†Echinodon Owen, 1861 |
| Species | |
Echinodon (pronounced eh-KY-no-don) meaning "hedgehog tooth" in reference to the spines on its teeth (Greek εχινος, echinos = hedgehog + όδους, odous = tooth), occasionally known as Saurechinodon, is a genus of small European dinosaur of the early Cretaceous Period (Berriasian age), 140 million years ago.
The type specimen was discovered by Samuel Beckles in the Purbeck Beds near Swanage, England. A bipedal herbivore, it was around 60 centimetres (2 ft) long. Unlike most ornithischians, Echinodon had one or two caniniform teeth in each maxilla.
The only species is E. becklesii, named in 1861 by Richard Owen, who mistook it for a lizard. Remains of an Echinodon-like animal were found in stratigraphic zone 4 of the Morrison Formation. These are now named Fruitadens.
Echinodon has at times been considered a basal thyreophoran, mainly due to the erroneous association of turtle limb osteoderms with its remains. Paul Sereno's reclassification to Heterodontosauridae in 1991 remains somewhat controversial. David B. Norman and Paul M. Barrett redescribed Echinodon in 2002 and supported the heterodontosaurid classification, though using somewhat different evidence than Sereno.
The cladogram below follows the analysis by Butler et al., 2011:
Echinodon
NHM RU A100
...
Wikipedia
