Encephalocele
| Encephalocele | |
|---|---|
 |
|
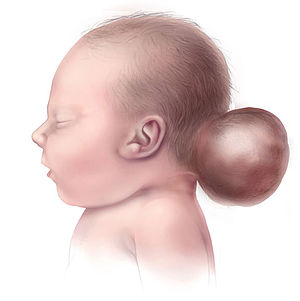
| Illustration of a child with encephalocele | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q01 |
| DiseasesDB | 29394 |
| eMedicine | radio/246 |
| MeSH | D004677 |
Encephalocele, sometimes known as cranium bifidum, is a neural tube defect characterized by sac-like protrusions of the brain and the membranes that cover it through openings in the skull. These defects are caused by failure of the neural tube to close completely during fetal development. Encephaloceles cause a groove down the middle of the skull, or between the forehead and nose, or on the back side of the skull. The severity of encephalocele varies, depending on its location.
Encephaloceles are often accompanied by craniofacial abnormalities or other brain malformations. Symptoms may include neurologic problems, hydrocephalus (cerebrospinal fluid accumulated in the brain), spastic quadriplegia (paralysis of the limbs), microcephaly (an abnormally small head), ataxia (uncoordinated muscle movement), developmental delay, vision problems, mental and growth retardation, and seizures.
A neonate with a large encephalocele.
Encephalocele on the head of a two-year-old.
Although the exact cause is unknown, encephaloceles are caused by failure of the neural tube to close completely during fetal development. Research has indicated that teratogens (substances known to cause birth defects), trypan blue (a stain used to color dead tissues or cells blue), and arsenic may damage the developing fetus and cause encephaloceles.
Proper levels of folic acid have been shown to help prevent such defects when taken before pregnancy, and early in pregnancy.
Usually encephaloceles are noticeable deformities and are diagnosed immediately after birth, but a small encephalocele in the nasal or forehead region can go undetected. Various physical and mental developmental delays can indicate the presence of encephaloceles.
Encephaloceles of the face are generally classified as nasofrontal, nasoethmoidal, or naso-orbital, however, there can be some overlap in the type of encephalocele. They can also appear along any part of the cranial vault as they result from abnormal closure of cranial bones; the most common location for enncephaloceles is the occipital region. If the bulging portion contains only cerebrospinal fluid and the overlying membrane, it may be called a meningocele. If brain tissue is present, it may be referred to as a meningoencephalocele.
...
Wikipedia
