Erucic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
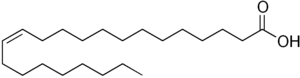
(Z)-Docos-13-enoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
112-86-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:28792 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1173380 |
| ChemSpider |
4444561 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.647 |
| KEGG |
C08316 |
| PubChem | 5281116 |
| UNII |
075441GMF2 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C22H42O2 | |
| Molar mass | 338.58 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White waxy solid |
| Density | 0.860 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 33.8 °C (92.8 °F; 306.9 K) |
| Boiling point | 381.5 °C (718.7 °F; 654.6 K) (decomposes) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in methanol and ethanol | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 349.9 °C (661.8 °F; 623.0 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Erucic acid is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, denoted 22:1ω9. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)11COOH. It is prevalent in wallflower seed with a reported content of 20 to 54% in high erucic acid rapeseed oil, and 42% in mustard oil. Erucic acid is also known as cis-13-docosenoic acid and the trans isomer is known as brassidic acid.
Erucic acid has many of the same uses as mineral oils, but it is more readily biodegradable than some. It has limited ability to polymerize and dry for use in oil paints. Like other fatty acids, it can be converted into surfactants or lubricants, and can be used as a precursor to biodiesel fuel.
Derivatives of erucic acid have many further uses, such as behenyl alcohol (CH3(CH2)21OH), a pour point depressant (enabling liquids to flow at a lower temperature), and silver behenate, for use in photography.
The name 'erucic' means: of or pertaining to Eruca; which is a genus of flowering plants in the family Brassicaceae. It is also the Latin for colewort, which today is better known as kale.
Erucic acid is produced naturally (together with other fatty acids) across a great range of green plants, but especially so in members of the Brassica genus. For industrial purposes, a 'low-erucic acid rapeseed' (LEAR) has been developed (canola), which contains fats derived from oleic acid instead of erucic acid.
...
Wikipedia
