European colonies in India
Imperial entities of India
|
|
| Dutch India | 1605–1825 |
|---|---|
| Danish India | 1620–1869 |
| French India | 1668–1954 |
|
|
|
| Casa da Índia | 1434–1833 |
| Portuguese East India Company | 1628–1633 |
|
|
|
| East India Company | 1612–1757 |
| Company rule in India | 1757–1858 |
| British Raj | 1858–1947 |
| British rule in Burma | 1824–1948 |
| Princely states | 1721–1949 |
| Partition of India |
1947
|
|
|
|
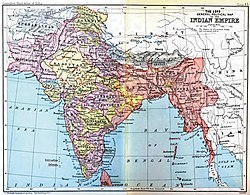
Colonial India is the part of South Asia which was under the jurisdiction of European colonial powers, through trade and conquest. The spice trade between India and Europe was one of the main types of trade in the world economy and was the main catalyst for the period of European exploration. The search for the wealth and prosperity of India led to the discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus in 1492 CE. Only a few years later, near the end of the 15th century, Portuguese sailor Vasco da Gama became the first European to re-establish direct trade links with India since Roman times by being the first to arrive by circumnavigating Africa (c. 1497–1499). Having arrived in Calicut, which by then was one of the major trading ports of the eastern world, he obtained permission to trade in the city from Saamoothiri Rajah.
Trading rivalries among the seafaring European powers brought other European powers to India. The Dutch Republic, England, France, and Denmark-Norway all established trading posts in India in the early 17th century. As the Mughal Empire disintegrated in the early 18th century, and then as the Maratha Empire became weakened after the third battle of Panipat, many relatively weak and unstable Indian states which emerged were increasingly open to manipulation by the Europeans, through dependent Indian rulers.
In the later 18th century Great Britain and France struggled for dominance, partly through proxy Indian rulers but also by direct military intervention. The defeat of the redoubtable Indian ruler Tipu Sultan in 1799 marginalised the French influence. This was followed by a rapid expansion of British power through the greater part of the Indian subcontinent in the early 19th century. By the middle of the century the British had already gained direct or indirect control over almost all of India. British India, consisting of the directly-ruled British presidencies and provinces, contained the most populous and valuable parts of the British Empire and thus became known as "the jewel in the British crown".
...
Wikipedia
