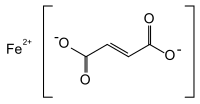
Ferrous fumarate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(E)-But-2-enedioate; iron(2+)
|
|
| Other names
Ferrous fumarate; Feostat
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.953 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H2FeO4 | |
| Molar mass | 169.90128 |
| Appearance | reddish-brown powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.435 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) |
| slightly soluble | |
| Pharmacology | |
| B03AA02 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
3850 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Iron(II) fumarate, also known as ferrous fumarate, is the iron(II) salt of fumaric acid, occurring as a reddish-orange powder, used to supplement iron intake. It has the chemical formula C4H2FeO4. Pure ferrous fumarate has an iron content of 32.87%, therefore one tablet of 300 mg iron fumarate will contain 98.6 mg of iron (548% Daily Value based on 18 mg RDI).
Ferrous fumurate is often taken by mouth as an iron supplement.
...
Wikipedia

