Flexor digitorum superficialis
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Details | |
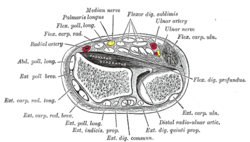
| Origin | medial epicondyle of the humerus (common flexor tendon) as well as parts of the radius and ulna. |
| Insertion | anterior margins on the bases of the middle phalanges of the four fingers |
| Artery | ulnar artery |
| Nerve | median nerve |
| Actions | flexor of fingers (primarily at proximal interphalangeal joints) |
| Antagonist | Extensor digitorum muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus flexor digitorum superficialis |
| TA | A04.6.02.033 |
| FMA | 38469 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
Flexor digitorum superficialis (flexor digitorum sublimis) is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is sometimes considered to be the deepest part of the superficial layer of this compartment, and sometimes considered to be a distinct, "intermediate layer" of this compartment. It is relatively common for the Flexor digitorum superficialis to be missing from the little finger, bilaterally and unilaterally, which can cause problems when diagnosing a little finger injury.
The muscle has two classically described heads - the humeroulnar and radial - and it is between these heads that the median nerve and ulnar artery pass. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint gives its origin to part of this muscle.
Four long tendons come off this muscle near the wrist and travel through the carpal tunnel formed by the flexor retinaculum. These tendons, along with those of flexor digitorum profundus, are enclosed by a common flexor sheath. The tendons attach to the anterior margins on the bases of the intermediate phalanges of the four fingers. These tendons have a split (Camper's Chiasm) at the end of them through which the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus pass.
The Flexor digitorium superficialis muscle is innervated by the median nerve (C7, C8, T1).
The primary function of flexor digitorum superficialis is flexion of the middle phalanges of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints, however under continued action it also flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints and wrist joint.
...
Wikipedia
