Foscarnet
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Foscavir |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601144 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Protein binding | 14-17% |
| Biological half-life | 3.3-6.8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | phosphonomethanoic acid, dihydroxyphosphinecarboxylic acid oxide |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.224.300 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | CH3O5P |
| Molar mass | 126.005 g/mol 300.1 g/mol (foscarnet trisodium hexahydrate) |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
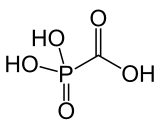
Foscarnet is the conjugate base of the chemical compound with the formula HO2CPO3H2. Foscarnet sodium is used as an antiviral medication.
Foscarnet was approved for medical use in 1991.
This phosphonic acid derivative (marketed by Clinigen as foscarnet sodium under the trade name Foscavir) is an antiviral medication used to treat herpes viruses, including drug-resistant cytomegalovirus (CMV) and herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2). It is particularly used to treat CMV retinitis. Foscarnet can be used to treat highly treatment-experienced patients with HIV as part of salvage therapy.
Foscarnet is a structural mimic of the anion pyrophosphate that selectively inhibits the pyrophosphate binding site on viral DNA polymerases at concentrations that do not affect human DNA polymerases.
In individuals treated with the DNA polymerase inhibitors acyclovir or ganciclovir, HSV or CMV particles can develop mutant protein kinases (thymidine kinase or UL97 protein kinase, respectively) that make them resistant to these antiviral drugs. However, unlike acyclovir and ganciclovir, foscarnet is not activated by viral protein kinases, making it useful in acyclovir- or ganciclovir-resistant HSV and CMV infections.
However, acyclovir- or ganciclovir-resistant mutants with alterations in viral DNA polymerase may also be resistant to foscarnet.
...
Wikipedia
