German languages
| Germanic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution |
Principally northern, western and central Europe, the Americas (Anglo-America, Caribbean Netherlands and Suriname), Southern Africa and Oceania |
| Linguistic classification |
Indo-European
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Germanic |
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-5 | |
| Linguasphere | 52- (phylozone) |
| Glottolog | germ1287 |
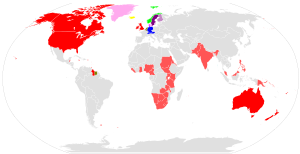
The Germanic languages by country
English most spoken native language
English official but not primary language
German most spoken native language
Dutch most spoken native language
Swedish most spoken native language
Swedish official but not primary language
Danish most spoken native language
Danish official but not primary language
Norwegian most spoken native language
Icelandic most spoken native language
|
|
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of approximately 500 million people mainly in North America, Oceania, Southern Africa, and Central, Western and Northern Europe.
The West Germanic branch includes the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with approximately 360–400 million native speakers,German with over 100 million native speakers, and Dutch with 23 million native speakers. Other major West Germanic languages are Afrikaans—an offshoot of Dutch—with over 7.1 million native speakers,Low German with roughly 6.7 million native speakers (considered a separate collection of dialects; 5 million in Germany and 1.7 million in the Netherlands),Yiddish—once used by approximately 13 million Jews in pre-World War II Europe —and Scots, both with 1.5 million native speakers. Limburgish varieties have roughly 1.3 million speakers along the Dutch–Belgian–German border.
The main North Germanic languages are Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Faroese, which have a combined total of about 20 million speakers.
...
Wikipedia
