Grand Duchy of Lithuania
| Grand Duchy of Lithuania | ||||||||||
| Part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795) | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
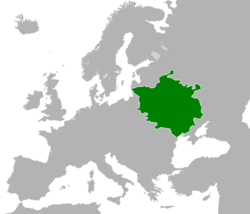
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania at the height of its power in the 15th century, superimposed on modern borders
|
||||||||||
| Capital | ||||||||||
| Languages | Lithuanian, Ruthenian, Polish, Latin, German (see § Languages) | |||||||||
| Religion | ||||||||||
| Government |
|
|||||||||
| Grand Duke | ||||||||||
| • | 1236–1263 (from 1251 as King) | Mindaugas (first) | ||||||||
| • | 1764–1795 | Stanisław August Poniatowski (last) | ||||||||
| Legislature | Seimas | |||||||||
| • | Privy Council | Council of Lords | ||||||||
| History | ||||||||||
| • | Consolidation began | 1180s | ||||||||
| • | Kingdom of Lithuania | 1251–1263 | ||||||||
| • | Union of Krewo | 14 August 1385 | ||||||||
| • | Union of Lublin | 1 July 1569 | ||||||||
| • | Third Partition | 24 October 1795 | ||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||
| • | 1260 | 200,000 km² (77,220 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 1430 | 930,000 km² (359,075 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 1572 | 320,000 km² (123,553 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 1791 | 250,000 km² (96,526 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 1793 | 132,000 km² (50,965 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||
| • | 1260 est. | 400,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 2 /km² (5.2 /sq mi) | |||||||||
| • | 1430 est. | 2,500,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 2.7 /km² (7 /sq mi) | |||||||||
| • | 1572 est. | 1,710,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 5.3 /km² (13.8 /sq mi) | |||||||||
| • | 1791 est. | 2,500,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 10 /km² (25.9 /sq mi) | |||||||||
| • | 1793 est. | 1,800,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 13.6 /km² (35.3 /sq mi) | |||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Today part of | ||||||||||
|
1. Unsuccessful Constitution of May 3, 1791 envisioned a unitary state whereby the Grand Duchy would be abolished.
2. Internationally recognized as part of Moldova. |
||||||||||
2. Internationally recognized as part of Moldova.
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 13th century until 1795. The state was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija.
The Grand Duchy later expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other Slavic lands, including territory of present-day Belarus, parts of Ukraine, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multi-confessional state with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage.
Consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 12th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in the religious crusade by the Teutonic Knights and the Livonian Order. The multi-ethnic and multi-confessional state emerged only at the late reign of Gediminas and continued to expand under his son Algirdas. Algirdas's successor Jogaila signed the Union of Krewo in 1386, bringing two major changes in the history of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania: conversion to Catholicism and establishment of a dynastic union between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland.
...
Wikipedia