Hebrew-language
| Hebrew | |
|---|---|
| עברית, Ivrit | |

|
|
| Pronunciation | [(ʔ)ivˈʁit] – [(ʔ)ivˈɾit] |
| Native to | Israel |
| Region | Land of Israel |
| Ethnicity | Israelites; Jews and Samaritans |
| Extinct | Ancient Hebrew extinct by 586 CE, surviving as a liturgical language for Judaism |
| Revival | 9.0 million speakers of Modern Hebrew of which 5 million are native speakers in Israel. (2016) |
|
Early forms
|
|
|
Standard forms
|
|
|
Hebrew alphabet Paleo-Hebrew alphabet (Archaic Biblical Hebrew) Imperial Aramaic script (Late Biblical Hebrew) |
|
| Signed Hebrew (oral Hebrew accompanied by sign) | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
| Regulated by |
Academy of the Hebrew Language האקדמיה ללשון העברית (HaAkademia LaLashon HaʿIvrit) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | he |
| ISO 639-2 | heb |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously: |
| Glottolog | hebr1246 |
| Linguasphere | 12-AAB-a |
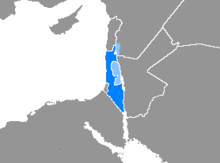
The Hebrew-speaking world:
regions where Hebrew is the language of the majority
regions where Hebrew is the language of a significant minority
|
|
Hebrew (/ˈhiːbruː/; עִבְרִית, Ivrit [ʔivˈʁit] (![]() listen) or [ʕivˈɾit] (
listen) or [ʕivˈɾit] (![]() listen)) is a Northwest Semitic language native to Israel, spoken by over 9 million people worldwide. Historically, it is regarded as the language of the Israelites and their ancestors, although the language was not referred to by the name Hebrew in the Tanakh. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date from the 10th century BCE. Hebrew belongs to the West Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Hebrew is the only living Canaanite language left, and the only truly successful example of a revived dead language.
listen)) is a Northwest Semitic language native to Israel, spoken by over 9 million people worldwide. Historically, it is regarded as the language of the Israelites and their ancestors, although the language was not referred to by the name Hebrew in the Tanakh. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date from the 10th century BCE. Hebrew belongs to the West Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Hebrew is the only living Canaanite language left, and the only truly successful example of a revived dead language.
...
Wikipedia
