Hindi-language
| Hindi | |
|---|---|
|
Hindī |
|

The word "Hindi" in Devanagari script
|
|
| Pronunciation | Hindustani pronunciation: [ˈɦin̪d̪iː] |
| Native to | North and North Western India |
|
Native speakers
|
260 million (2001) L2 speakers: 120 million (1999) |
|
Early forms
|
Sauraseni Prakrit
|
|
Devanagari Devanagari Braille |
|
| Signed Hindi | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
|
Recognised minority
language in |
|
| Regulated by | Central Hindi Directorate |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | hi |
| ISO 639-2 | |
| ISO 639-3 | |
|
Linguist list
|
hin-hin |
| Glottolog | hind1269 |
| Linguasphere | 59-AAF-qf |
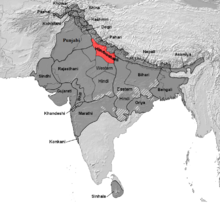
Areas (red) where Hindustani (Khariboli/Kauravi) is the native language, compared to all Indo-Aryan languages (dark grey)
|
|
Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: मानक हिन्दी, IAST: Mānak Hindī) or simply Hindi (Devanagari: , IAST: Hindī), is an Indo-Aryan language and a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language. Hindi is one of the official languages of India, and is the lingua franca of the Hindi belt languages. Outside India, Hindi is an official language in Fiji, and is a recognised regional language in Mauritius, Suriname, Guyana, and Trinidad and Tobago.
Hindi is the fourth most-spoken first language in the world, after Standard Mandarin Chinese, Spanish and English.
Part XVII of the Indian Constitution deals with Official Language. Under Article 343, official language of the Union has been prescribed, which includes Hindi in Devanagari script and English.
Gujarat High Court, in 2010, has observed that there was nothing on record to suggest that any provision has been made or order issued declaring Hindi as a national language of India.
Article 343 of the Indian constitution states
(1) The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals.
...
Wikipedia
