Insulin pump
| Insulin pump | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
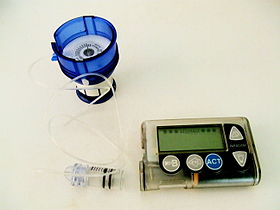
Insulin pump, showing an infusion set loaded into spring-loaded insertion device. A reservoir is attached to the infusion set (shown here removed from the pump).
|
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy. The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump includes:
Other configurations are possible. For instance, more recent models may include disposable or semi-disposable designs for the pumping mechanism and may eliminate tubing from the infusion set.
An insulin pump is an alternative to multiple daily injections of insulin by insulin syringes or an insulin pen and allows for intensive insulin therapy when used in conjunction with blood glucose monitoring and carb counting.
Insulin pumps, cartridges, and infusion sets may be far more expensive than syringes used for insulin injection with several insulin pumps costing more than $6,000; necessary supplies can cost over $300. Another disadvantage of insulin pump use is a higher risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis if the pump malfunctions. This can happen if the pump battery is discharged, if the insulin is inactivated by heat exposure, if the insulin reservoir runs empty, the tubing becomes loose and insulin leaks rather than being injected, or if the cannula becomes bent or kinked in the body, preventing delivery. Therefore, pump users typically monitor their blood sugars more frequently to evaluate the effectiveness of insulin delivery.
Use of insulin pumps is increasing because of:
In 1963 Dr. Arnold Kadish designed the first insulin pump to be worn as a backpack. A more wearable version was later devised by Dean Kamen in 1976. Kamen formed a company called "AutoSyringe" to market the product, which he sold to Baxter Health Care in 1981.
The insulin pump was first endorsed in the United Kingdom in 2003, by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
...
Wikipedia
