Liver impairment
| Hepatic disease | |
|---|---|
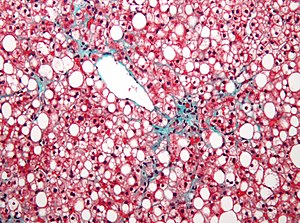 |
|
| Micrograph of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| MedlinePlus | 000205 |
Liver disease (also called hepatic disease) is a type of damage to or disease of the liver.
There are more than a hundred different kinds of liver disease,symptoms may include jaundice and weight loss. These are some of the most common:
Liver disease can occur through several mechanisms. A common form of liver disease is viral infection. Viral hepatitides such as Hepatitis B virus and Hepatitis C virus can be vertically transmitted during birth via contact with infected blood. According to a 2012 NICE publication, "about 85% of hepatitis B infections in newborns become chronic". In occult cases, Hepatitis B virus is present by HBV DNA, but testing for HBsAg is negative. High consumption of alcohol can lead to several forms of liver disease including alcoholic hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. In the earlier stages of alcoholic liver disease, fat builds up in the liver's cells due to increased creation of triglycerides and fatty acids and a decreased ability to break down fatty acids. Progression of the disease can lead to liver inflammation from the excess fat in the liver. Scarring in the liver often occurs as the body attempts to heal and extensive scarring can lead to the development of cirrhosis in more advanced stages of the disease. Approximately 3–10% of individuals with cirrhosis develop a form of liver cancer known as .
According to Tilg, et al., gut microbiome could very well have an effect, be involved in the pathophysiology, on the various types of liver disease which an individual may encounter.
...
Wikipedia
