Orbivirus
| Orbivirus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
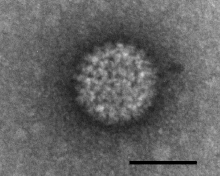
| Negatively stained bluetongue virus–like particle that caused a cytopathic effect in BHK-21 cells. Scale bar = 50 nm | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group III (dsRNA) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | Reoviridae |
| Subfamily: | Sedoreovirinae |
| Genus: | Orbivirus |
| Type Species | |
The genus Orbivirus is a member of the Reoviridae family, in the subfamily Sedoreovirinae. Unlike the other reoviruses, orbiviruses are arboviruses. This genus currently contains 22 species (including the type species Bluetongue virus) and at least 130 different serotypes. Orbiviruses can infect and replicate within a wide range of arthropod and vertebrate hosts. Orbiviruses are named after their characteristic doughnut shaped capsomers (Orbi in Latin means ring).
Many orbiviruses are transmitted by ticks or haematophagus insect vectors (Culicoides, mosquitoes and sand flies) and have a wide host range that includes cattle, goats and sheep, wild ruminants, equids, camelids, marsupials, sloths, bats, birds, large canine and feline carnivores and humans.
The three economically most important orbiviruses are Bluetongue virus, African horse sickness virus and epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus all of which are transmitted by Culicoides species.
...
Wikipedia
