PFPP
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 6–8 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
64090-19-3 2252-63-3, 64090-19-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 75260 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
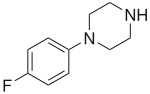
| Formula | C10H13FN2 |
| Molar mass | 180.222 g/mol |
para-Fluorophenylpiperazine (pFPP, 4-FPP, 4-Fluorophenylpiperazine; Fluoperazine, Flipiperazine) is a piperazine derivative with mildly psychedelic and euphoriant effects. It has been sold as an ingredient in legal recreational drugs known as "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.
pFPP has been found in vitro to act mainly as a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, with some additional affinity for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, and to possibly induce their release.
pFPP was originally discovered as a metabolite of the hypnotic antihistamine niaprazine in 1982, but was rediscovered in 2003 as a potential recreational drug, and sold as an ingredient in "Party pills" in New Zealand, under brand names such as "The Big Grin", "Mashed", and "Extreme Beans". Subsequently it has continued to be used as an ingredient in black market "ecstasy" pills around the world.
pFPP has little stimulant effects, with its subjective effects derived mainly from its action as a 5-HT1A receptor agonist. pFPP is active at doses between 20 and 150 mg, but higher doses cause a range of side-effects such as migraine headaches, muscle aches, anxiety, nausea, and vomiting. Metabolic studies have shown pFPP to be an inhibitor of various enzymes in the liver which may contribute to its side-effect profile.
...
Wikipedia
