Pegomastax
|
Pegomastax Temporal range: Early Jurassic, 200–190 Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
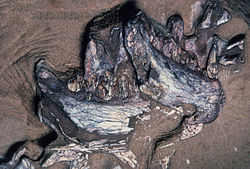
| Lower jaws of specimen SAM-PK-K10488 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | †Ornithischia |
| Family: | †Heterodontosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Heterodontosaurinae |
| Genus: |
†Pegomastax Sereno, 2012 |
| Type species | |
|
†Pegomastax africana Sereno, 2012 |
|
Pegomastax ("strong jaw") is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur discovered in Lower Jurassic rocks in South Africa. It is based on SAM-PK-K10488, a partial skull including a postorbital bone, both dentaries (the tooth-bearing bone of the lower jaw), and a predentary (a toothless beak-like bone found at the tip of the lower jaw). From head to tail the parrot-like herbivore measured no more than 60 cm.
This specimen was found in Voyizane, Joe Gqabi District, Cape Province, in rocks of the upper Elliot Formation, a rock formation that dates to the early part of the Early Jurassic (Hettangian–Sinemurian, approximately 200 to 190 million years ago). It was collected during a 1966–1967 expedition but not formally named and described until 2012, when Paul Sereno, who had recognized it as unusual in the 1980s, published a description. The type species is P. africana.Pegomastax differed from other heterodontosaurids by details of the skull. The lower jaw was robust, with a short beak. Like most other heterodontosaurids, Pegomastax had an enlarged canine-like tooth at the beginning of the lower jaw's tooth row, which may have had a defensive function.
...
Wikipedia
