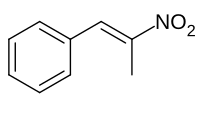
Phenyl-2-nitropropene
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1-Phenyl-2-nitropropene
|
|
| Other names
P2NP, β-methyl-β-nitropropene, (2-Nitro-1-propenyl)benzene
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.731 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 163.17 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | solid |
| Melting point | 64 to 66 °C (147 to 151 °F; 337 to 339 K) |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Harmful (Xn) |
| R-phrases | R22, R36/37/38 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Phenyl-2-nitropropene is a chemical compound with the chemical formula is C9H9NO2. It can be produced by the reaction of benzaldehyde and nitroethane in the presence of a basic catalyst. In this reaction, the base deprotonates nitroethane to form a resonance stabilized anion. This anion nucleophilically adds to the aldehyde forming a beta nitro alcohol, which is subsequently dehydrated to yield the nitroalkene. This reaction is known as a nitroaldol reaction. Phenyl-2-nitropropene is used to make pharmaceuticals. It is used in pharmaceutical industry to manufacture drug Adderall, which is used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy.
...
Wikipedia
