Phenylpropanoid biochemical pathway
The metabolic pathway of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes.
The shikimate pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by bacteria, fungi, and plants for the biosythesis of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan).
In plants, the biosynthesis of all phenylpropanoids begins with the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine.
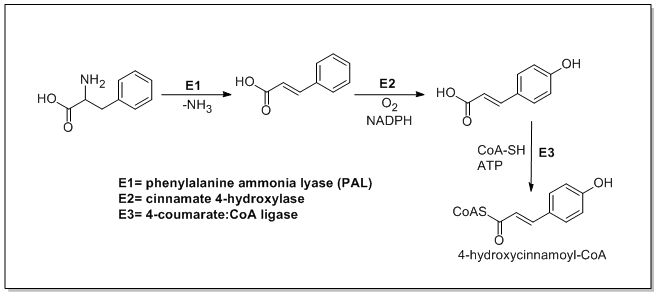
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a. phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase) is an enzyme responsible for the transformation of L-phenylalanine or tyrosine into trans-cinnamic acid or p-coumaric acid respectively and ammonia.
Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (cinnamate 4-hydroxylase) is the enzyme responsible for the transformation of trans-cinnamate into 4-hydroxycinnamate (p-coumaric acid). 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase is the enzyme responsible for the transformation of 4-coumarate (p-coumaric acid) into 4-coumaroyl-CoA.
An alternative bacterial ketosynthase-directed stibenoids biosynthesis pathway exists in Photorhabdus bacterial symbionts of Heterorhabditis nematodes, producing 3,5-dihydroxy-4-isopropyl-trans-stilbene for antibiotic purposes.
...
Wikipedia