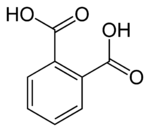
Phthalic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid
|
|
| Other names
1,2-Benzenedioic acid
Phthalic acid Benzene-1,2-dioic acid ortho-Phthalic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
88-99-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:29069 |
| ChemSpider |
992 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.703 |
| EC Number | 201-873-2 |
| PubChem | 1017 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 166.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.593 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K) |
| 0.6 g / 100 mL | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.89, 5.51 |
| -83.61·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related carboxylic acids
|
Isophthalic acid Terephthalic acid |
|
Related compounds
|
Phthalic anhydride Phthalimide Phthalhydrazide Phthaloyl chloride Benzene-1,2- dicarboxaldehyde |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Phthalic acid is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. It is an isomer of isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid. Although phthalic acid is of modest commercial importance, the closely related derivative phthalic anhydride is a commodity chemical produced on a large scale.
Phthalic acid is produced by the catalytic oxidation of naphthalene or ortho-xylene directly to phthalic anhydride and a subsequent hydrolysis of the anhydride.
Phthalic acid was first obtained by French chemist Auguste Laurent in 1836 by oxidizing naphthalene tetrachloride. Believing the resulting substance to be a naphthalene derivative, he named it "naphthalic acid". After the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac determined its correct formula, Laurent gave it its present name. Manufacturing methods in the nineteenth century included oxidation of naphthalene tetrachloride with nitric acid, or, better, oxidation of the hydrocarbon with fuming sulfuric acid, using mercury or mercury(II) sulfate as a catalyst.
It is a dibasic acid, with pKa's of 2.89 and 5.51. The monopotassium salt, potassium hydrogen phthalate is a standard acid in analytical chemistry. Typically phthalate esters are prepared from the widely available phthalic anhydride. Reduction of phthalic acid with sodium amalgam in the presence of water gives the 1,3-cyclohexadiene derivative.
...
Wikipedia

