Potassium superoxide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Potassium dioxide
|
|
| Other names
Potassium superoxide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
12030-88-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider |
8329498 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.574 |
| EC Number | 234-746-5 |
| PubChem | 61541 |
| RTECS number | TT6053000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| KO2 | |
| Molar mass | 71.10 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 2.14 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 560 °C (1,040 °F; 833 K) (decomposes) |
| decomposes | |
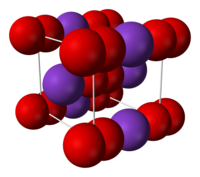
| Structure | |
| Body-centered cubic (O− 2) |
|
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
117 J·mol−1·K−1 |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−283 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | corrosive, oxidant |
| R-phrases | 8-14-34 |
| S-phrases | 17-27-36/37/39 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Potassium oxide Potassium peroxide |
|
Other cations
|
Sodium superoxide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Potassium superoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula KO
2. It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide ion. Potassium superoxide is used as a CO
2 scrubber, H
2O dehumidifier and O
2 generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines and spacesuit life support systems.
Potassium superoxide is produced by burning molten potassium in an atmosphere of oxygen.
The salt consists of K+
and O−
2 ions, linked by ionic bonds. The O-O distance is 1.28 Å.
Hydrolysis gives oxygen gas, hydrogen peroxide and potassium hydroxide:
Its degradation by carbon dioxide affords carbonates:
Combinations of these two reactions occur as well:
Potassium superoxide finds only niche uses as a laboratory reagent. Because it reacts with water, KO
2 is often studied in organic solvents. Since the salt is poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents, crown ethers are typically used. The tetraethylammonium salt is also known. Representative reactions of these salts involve the use of superoxide as a nucleophile, e.g., in the conversion of alkyl bromides to alcohols and acyl chlorides into diacyl peroxides.
...
Wikipedia

