Prunasin
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
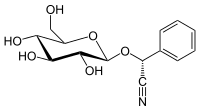
(2R)-2-Phenyl-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyacetonitrile
|
|
| Other names
(R)-Prunasin
D-Prunasin D-Mandelonitrile-β-D-glucoside |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.489 |
| EC Number | 202-738-0 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C14H17NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 295.29 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Prunasin is a cyanogenic glycoside related to amygdalin.
Prunasin is found in species in the genus Prunus such as Prunus japonica or P. maximowiczii and in bitter almonds. It is also found in leaves and stems of Olinia ventosa, O. radiata, O. emarginata and O. rochetiana and in Acacia greggii.
It is also found in dandelion coffee, a coffee substitute.
Prunasin is hydrolyzed to produce hydrogen cyanide. Plants containing prunasin may therefore be toxic to animals, particularly ruminants.
Prunasin beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that uses (R)-prunasin and H2O to produce D-glucose and mandelonitrile.
Amygdalin beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that uses (R)-amygdalin and H2O to produce (R)-prunasin and D-glucose.
...
Wikipedia
