Pulmonary artery pressure
| Pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Precursor | truncus arteriosus |
| System | Cardiovascular, Respiratory |
| Source | right ventricle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria pulmonalis |
| MeSH | A07.231.114.715 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
t_20/12826098 |
| FMA | 45842 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
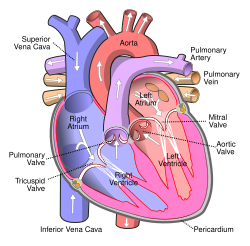
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are located next to the pulmonary alveoli.
In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk or main pulmonary artery. The main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short and wide—approximately 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in length and 3 centimetres (1.2 in) in diameter.
The main pulmonary artery splits into the right and the left main pulmonary artery. The left main pulmonary artery is shorter and somewhat smaller than the right, passes horizontally in front of the descending aorta and left bronchus to the root of the left lung. Above, the left main pulmonary artery is connected to the concavity of the proximal descending aorta by the ligamentum arteriosum. Below, the left main pulmonary artery is joined to the upper left pulmonary vein by the ligament of the left vena cava. It divides into two lobar arteries, one for each lobe of the left lung. The right main pulmonary artery follows a longer and more horizontal course as it crosses the mediastinum. It passes underneath the aortic arch, behind the ascending aorta, and in front of the descending aorta. It courses posterior to the superior vena cava and in front of the right bronchus. Upon reaching the right pulmonary hila, the right main pulmonary artery divides into two branches:
The right and left main pulmonary arteries give off branches that roughly correspond to the lung lobes, and can in such cases be termed lobar arteries. The lobar arteries branch into segmental arteries (roughly 1 for each lobe segment), which in turn branch into subsegmental pulmonary arteries. These eventually form intralobular arteries.
The pulmonary arteries originate from the truncus arteriosus and the sixth pharyngeal arch. The truncus arteriosis is a structure that forms during the development of the heart as a successor to the conus arteriosus.
...
Wikipedia