Pyrogallic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2,3-triol
|
|
| Other names
1,2,3-Trihydroxybenzene
Pyrogallic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.603 |
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 126.11 g/mol |
| Density | 1.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 131 to 134 °C (268 to 273 °F; 404 to 407 K) |
| Boiling point | 309 °C (588 °F; 582 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Pyrogallol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a white water-soluble solid although samples are typically brownish because of its sensitivity toward oxygen. It is one of three isomeric benzenetriols.
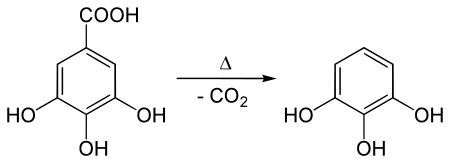
It is produced in the manner it was first prepared by Scheele (1786): heating gallic acid. Presently gallic acid is obtained from tannin. Heating induces decarboxylation:
Because tannin is expensive, many alternative routes have been devised. An alternate preparation involves treating para-chlorophenoldisulphonic acid with potassium hydroxide, a variant on the time-honored route to phenols from sulfonic acids.
The aquatic plant Myriophyllum spicatum produces pyrogallic acid.
When in alkaline solution, it absorbs oxygen from the air, turning brown from a colourless solution. It can be used in this way to calculate the amount of oxygen in air, notably via the use of the Orsat apparatus.
One can find its uses in hair dying, dying of suturing materials and for oxygen absorption in gas analysis. It also has antiseptic properties. Pyrogallol was also used as a developing agent in black-and-white developers, but its use is largely historical except for special purpose applications. (Hydroquinone is more commonly used today.)
...
Wikipedia