Renal vein
| Renal vein | |
|---|---|

The anterior surfaces of the kidneys, showing the areas of contact of neighboring viscera.
|
|
|
|
| Details | |
| Drains from | kidney |
|
Source
|
interlobar veins |
| Drains to | inferior vena cava |
| Artery | Renal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae renales |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.752 |
| TA | A12.3.09.009 |
| FMA | 14334 70899, 14334 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
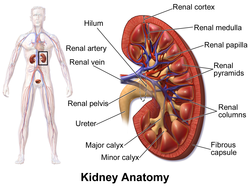
The renal veins are veins that drain the kidney. They connect the kidney to the inferior vena cava. They carry the blood filtered by the kidney.
There is one vein per kidney, that divides into 4 divisions upon entering the kidney:
Because the inferior vena cava is on the right half of the body, the left renal vein is generally the longer of the two.
Because the inferior vena cava is not laterally symmetrical, the left renal vein often receives the following veins:
This is in contrast to the right side of the body, where these veins drain directly into the IVC.
Often, each renal vein will have a branch that receives blood from the ureter.
It is usually singular to each kidney, except in the condition "multiple renal veins". In some people the left renal vein passes behind the abdominal aorta instead of in front of it, this is termed a retroaortic left renal vein, which is also known as "The Vein of Schnitker." If there is both a vein passing in front of and one behind the aorta this is called a circumaortic renal vein.
Diseases associated with the renal vein include renal vein thrombosis (RVT) and nutcracker syndrome (renal vein entrapment syndrome).
3D-rendered computed tomography, showing one renal vein (in red color) for each kidney
Frontal section through the kidney
Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries.
Renal vein
Human kidneys viewed from behind with spine removed.
Kidney
Renal vein
Renal vein
Renal vein
...
Wikipedia
