Salish languages
| Salishan | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution |
Pacific Northwest and Interior Plateau/Columbia Plateau in Canada and the United States |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | |
| Glottolog | sali1255 |
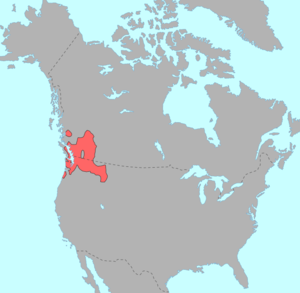
Pre-contact distribution of Salishan languages (in red).
|
|
The Salishan (also Salish) languages are a group of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America (the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana). They are characterised by agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk word xłp̓x̣ʷłtłpłłskʷc̓ (IPA: [xɬpʼχʷɬtʰɬpʰɬːskʷʰt͡sʼ]), meaning "he had had [in his possession] a bunchberry plant," has thirteen obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels. The Salishan languages are a geographically continuous block, with the exception of the Nuxalk (Bella Coola), in the Central Coast of British Columbia, and the extinct Tillamook language, to the south on the central coast of Oregon.
The terms Salish and Salishan are used interchangeably by linguists and anthropologists studying Salishan, but this is confusing in regular English usage. The name Salish or Selisch is the endonym of the Flathead Nation. Linguists later applied the name Salish to related languages in the Pacific Northwest. Many of the peoples do not have self-designations (autonyms) in their languages; they frequently have specific names for local dialects, as the local group was more important culturally than larger tribal relations.
...
Wikipedia
