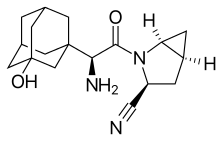
Saxagliptin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Onglyza |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a610003 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | A10BH03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~75% (Tmax = 2 h) |
| Protein binding | negligible |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4 and CYP3A5) |
| Biological half-life | 2.5 h (saxagliptin), 3.1 h (main metabolite) |
| Excretion | 22% (Bile), 75% (Urine) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
361442-04-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 11243969 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6316 |
| DrugBank |
DB06335 |
| ChemSpider |
9419005 |
| UNII |
8I7IO46IVQ |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL385517 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H25N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 315.41 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Saxagliptin (rINN), previously identified as BMS-477118, is an oral hypoglycemic (anti-diabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-Myers Squibb to co-develop the final compound and collaborate on the marketing of the drug. In June 2008, it was announced that Onglyza would be the trade name under which saxagliptin will be marketed.
In April 2016, the U.S. FDA added a warning about increased risk of heart failure. This was based on data in an article that concluded "DPP-4 inhibition with saxagliptin did not increase or decrease the rate of ischemic events, though the rate of hospitalization for heart failure was increased. Although saxagliptin improves glycemic control, other approaches are necessary to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with diabetes."
Saxagliptin is used as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It does not appear to decrease the risk of heart attacks or strokes. It increases the risk of hospitalization for heart failure by about 27%. Like other DPP-4 inhibitors, it has relatively modest HbA1c lowering ability, is associated with a relatively modest risk of hypoglycemia, and does not cause weight gain.
Saxagliptin improved mean HbA1c levels (relative to placebo) in a 24-week trial in people with type 2 diabetes. Combination therapy with saxagliptin and metformin was more effective than saxagliptin or metformin monotherapy. When the relative benefits of increasing the dose of a sulfonylurea or adding saxagliptin were assessed in a study of 768 patients, combination treatments were shown to have a significantly greater impact on fasting blood glucose than increasing the tested glibenclamide dose alone.
In those taking sulphonylureas there is an increased risk of low blood sugar.
...
Wikipedia
