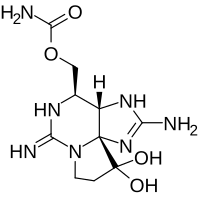
Saxitoxin
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(3aS-(3a-α,4-α,10aR*))-2,6-Diamino-4-(((amino-carbonyl)oxy)methyl)-3a,4,8,9-tetrahydro-1H,10H-pyrrolo(1,2-c)purine-10,10-diol
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
35523-89-8 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:34970 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL501134 |
||
| ChemSpider |
34106 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.160.395 | ||
| 2625 | |||
| KEGG |
C13757 |
||
| PubChem | 37165 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C10H17N7O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 299.29 g·mol−1 | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the human illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
The term saxitoxin originates from the genus name of the butter clam (Saxidomus) from which it was first isolated. But the term saxitoxin can also refer to the entire suite of more than 50 structurally related neurotoxins (known collectively as "saxitoxins") produced by algae and cyanobacteria which includes saxitoxin itself (STX), neosaxitoxin (NSTX), gonyautoxins (GTX) and decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX).
Saxitoxin has a large environmental and economic impact, as its presence in bivalve shellfish such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops frequently leads to bans on commercial and recreational shellfish harvesting in many temperate coastal waters around the world including northeastern and western United States, western Europe, east Asia, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. In the United States, paralytic shellfish poisoning has occurred in California, Oregon, Washington, Alaska, and New England.
Saxitoxin is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (Alexandrium sp., Gymnodinium sp., Pyrodinium sp.) and freshwater cyanobacteria (Anabaena sp., some Aphanizomenon spp., Cylindrospermopsis sp., Lyngbya sp., Planktothrix sp.) Saxitoxin accumulates particularly in bivalve filter feeders.
...
Wikipedia