Septula testis
| Septa of testis | |
|---|---|

A diagram of the major components of an adult human testicle, including the following numbered items: 1. Tunica albuginea, 2. Septula testis, 3. Lobulus testis, 4. Mediastinum testis, 5. Tubuli seminiferi contorti, 6. Tubuli seminiferi recti, 7. Rete testis, 8. Ductuli efferentes testis, 9a. Head of epididymis, 9b. Body of epididymis, 9.c Tail of epididymis,10. Vas deferens, 11a. Tunica vaginalis (parietal lamina), 11b. Tunica vaginalis (visceral lamina), and 12. Cavity of tunica vaginalis.
|
|
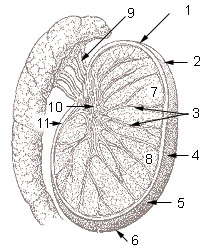
1: Head or upper pole of testis, 2: Tunica albuginea, 3: Testicular septa, 4: Anterior margin (free margin), 5: Lateral surface, 6: Tail or lower pole of testis, 7: Testicular lobules, 8: Parenchyma of testis, 9: Efferent ductules, 10: Mediastinum testis, 11: Posterior margin
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | septula testis |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
s_08/12730045 |
| TA | A09.3.01.019 |
| FMA | 19814 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
Each lobule of the testis is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa which extend between the mediastinum testis and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the tubuli seminiferi.
Transverse section through the left side of the scrotum and the left testis.
Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
...
Wikipedia
