Sleep-deprived
| Sleep deprivation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
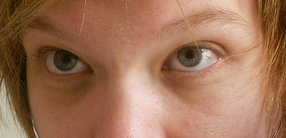
| Minor dark circles, in addition to a hint of eye bags - a combination suggestive of minor sleep deprivation. | |
| Specialty | Sleep medicine |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
Sleep deprivation is the condition of not having enough sleep; it can be either chronic or acute. A chronic sleep-restricted state can cause fatigue, daytime sleepiness, clumsiness and weight loss or weight gain. It adversely affects the brain and cognitive function. However, in a subset of cases sleep deprivation can, paradoxically, lead to increased energy and alertness and enhanced mood; it has even been used as a treatment for depression (see below).
Few studies have compared the effects of acute total sleep deprivation and chronic partial sleep restriction. Complete absence of sleep over long periods has not been seen in humans (unless they suffer from fatal familial insomnia); it appears that brief microsleeps cannot be avoided. Long-term total sleep deprivation has caused death in lab animals.
Generally, sleep deprivation may result in:
It has been suggested that people experiencing short-term sleep restrictions, process glucose more slowly than individuals receiving a full 8 hours of sleep, increasing the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. In 2005, a study of over 1400 participants showed that participants who habitually slept few hours were more likely to have associations with type 2 diabetes. However, because this study was merely correlational, the direction of cause and effect between little sleep and diabetes is uncertain. The authors point to an earlier study which showed that experimental rather than habitual restriction of sleep resulted in impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). Sleep deprivation can cause insulin resistance in the body, triggering the onset of early diabetes.
Sleep deprivation can adversely affect the brain and cognitive function. A 2000 study, by the UCSD School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Healthcare System in San Diego, used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) technology to monitor activity in the brains of sleep-deprived subjects performing simple verbal learning tasks. The study showed that regions of the brain's prefrontal cortex, an area that supports mental faculties such as working memory and logical and practical ("means-ends") reasoning, displayed more activity in sleepier subjects. Researchers interpreted this result as indicating that the brain of the average sleep-deprived subject had to work harder than that of the average non-sleep-deprived subject to accomplish a given task, and from this indication they inferred the conclusion the brains of sleep-deprived subjects were attempting to compensate for adverse effects caused by sleep deprivation.
...
Wikipedia
