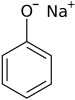
Sodium phenolate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium phenolate
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.862 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H5NaO | |
| Molar mass | 116.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Sodium phenoxide is an organic compound with the formula NaOC6H5. This white solid is the conjugate base of phenol. It is used as a precursor to many other organic compounds, such as aryl ethers.
Most commonly, solutions of sodium phenoxide are produced by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide. Anhydrous derivatives can be prepared from phenol and sodium:
Like other sodium alkoxides, crystalline sodium phenolate adopts a complex structure involving multiple Na-O bonds. Solvent-free material is polymeric, each Na center being bound to three oxygen ligands as well as the phenyl ring. Adducts of sodium phenoxide are molecular, such as the cubane [NaOPh]4(HMPA)4.
Sodium phenoxide is produced by the "alkaline fusion" of benzenesulfonic acid, whereby the sulfonate groups are displaced by hydroxide:
This route once was the principal industrial route to phenol.
...
Wikipedia


